점 B , D , J 는 직각삼각형 ACG 의 각변의 중점이다.
점 K , E , I 는 직각삼각형 JDG 의 각변의 중점이다.
삼각형을 이렇게 나누고, 색칠하기를 100번한다.
3번 까지는 그림에 그려져 있다.
AC = CG = 6, 색칠한 삼각형의 전체 넓이는 약 얼마인가?
AC = CG = 6, 색칠한 삼각형의 전체 넓이는 약 얼마인가?
(A) 6 (B) 7 (C) 8 (D) 9 (E) 10
(풀이)
(풀이 1)삼각형 CBD 의 넓이는 3*3/2 =9/2
삼각형 DKE 의 넓이는 9/8
삼각형 ELF 의 넓이는 9/32
색칠한 삼각형의 합은 9/2 + 9/8 + 9/32 = 189/32 = 5.9
삼각형 FGH 를 모두 색칠하면 9/32 만큼 더 더하면 된다.
합은 9/2 + 9/8 + 9/32 + 9/32 = 198/32 = 6.2
색칠한 삼각형의 전체 넓이는 5.9 와 6.2 사이에 있다.
답은 ( A) 6 이다.
(풀이 2)
사다리꼴 ACDJ 는 삼각형 3개중 한개인 BCD 에 색칠되어 있고,
사다리꼴 JDEI 는 삼각형 3개중 한개인 KDE 에 색칠되어 있고,
사다리꼴 IEFH 는 삼각형 3개중 한개인 LEF 에 색칠되어 있다.
이렇게 100번을 반복하면 각 사다리꼴의 1/3 이 색칠되어 있고 모두 합하면
삼각형 ACG의 넓이 6*6/2 = 18 의 3분의 1인 18/3 = 6 이다.
(풀이 3)
색칠한 삼각형의 전체 넓이는
9/2 + 9/8 + 9/32 + 9/128 + ............. = ?
a1 = 9/2, r = 1/4
초항 9/2 이고 , 공비 1/4 이다.
무한급수의 합은 S = a1/( 1- r ) = (9/2) / ( 1 - 1/4 ) = 6
(풀이 4)
변 AC 에 한점을 잡고 점 P라 하자.
점 P 와 점 G를 연결하면 대략 삼각형을 3등분 함을 알수있다.
((6*6)/2)/3 = 6
(풀이 5)
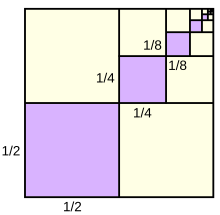
Each of the purple squares has 1/4 of the area of the next larger square
(1/2×1/2 = 1/4, 1/4×1/4 = 1/16, etc.).
The sum of the areas of the purple squares
is one third of the area of the large square.
Points B, D, and J are midpoints of the sides of right triangle ACG. Points K, E, I are midpoints of the sides of triangle JDG, etc. If the dividing and shading process is done 100 times (the first three are shown) and AC = CG = 6, then the total area of the shaded triangles is nearest
(풀이 1)삼각형 CBD 의 넓이는 3*3/2 =9/2
삼각형 DKE 의 넓이는 9/8
삼각형 ELF 의 넓이는 9/32
색칠한 삼각형의 합은 9/2 + 9/8 + 9/32 = 189/32 = 5.9
삼각형 FGH 를 모두 색칠하면 9/32 만큼 더 더하면 된다.
합은 9/2 + 9/8 + 9/32 + 9/32 = 198/32 = 6.2
색칠한 삼각형의 전체 넓이는 5.9 와 6.2 사이에 있다.
답은 ( A) 6 이다.
(풀이 2)
사다리꼴 ACDJ 는 삼각형 3개중 한개인 BCD 에 색칠되어 있고,
사다리꼴 JDEI 는 삼각형 3개중 한개인 KDE 에 색칠되어 있고,
사다리꼴 IEFH 는 삼각형 3개중 한개인 LEF 에 색칠되어 있다.
이렇게 100번을 반복하면 각 사다리꼴의 1/3 이 색칠되어 있고 모두 합하면
삼각형 ACG의 넓이 6*6/2 = 18 의 3분의 1인 18/3 = 6 이다.
(풀이 3)
색칠한 삼각형의 전체 넓이는
9/2 + 9/8 + 9/32 + 9/128 + ............. = ?
a1 = 9/2, r = 1/4
초항 9/2 이고 , 공비 1/4 이다.
무한급수의 합은 S = a1/( 1- r ) = (9/2) / ( 1 - 1/4 ) = 6
(풀이 4)
변 AC 에 한점을 잡고 점 P라 하자.
점 P 와 점 G를 연결하면 대략 삼각형을 3등분 함을 알수있다.
((6*6)/2)/3 = 6
(풀이 5)

(1/2×1/2 = 1/4, 1/4×1/4 = 1/16, etc.).
The sum of the areas of the purple squares
is one third of the area of the large square.
Points B, D, and J are midpoints of the sides of right triangle ACG. Points K, E, I are midpoints of the sides of triangle JDG, etc. If the dividing and shading process is done 100 times (the first three are shown) and AC = CG = 6, then the total area of the shaded triangles is nearest
(A) 6 (B) 7 (C) 8 (D) 9 (E) 10
Solution
Solution 1
Since FGH is fairly small relative to the rest of the diagram, we can make an underestimate by using the current diagram. All triangles are right-isosceles triangles.
The sum of the shaded regions is 
If you shade all of  , this will add an additional
, this will add an additional  to the area, giving
to the area, giving  , which is an overestimate.
, which is an overestimate.
Thus,  is the only answer that is both over the underestimate and under the overestimate.
is the only answer that is both over the underestimate and under the overestimate.
Solution 2
In iteration  , congruent triangles
, congruent triangles  and
and  are created, with one of them being shaded.
are created, with one of them being shaded.
In iteration  , three more congruent triangles are created, with one of them being shaded.
, three more congruent triangles are created, with one of them being shaded.
As the process continues indefnitely, in each row,  of each triplet of new congruent triangles will be shaded. The "fourth triangle" at the top (
of each triplet of new congruent triangles will be shaded. The "fourth triangle" at the top ( in the diagram) will gradually shrink,
in the diagram) will gradually shrink,
leaving about  of the area shaded. This means
of the area shaded. This means  square units will be shaded when the process goes on indefinitely, giving
square units will be shaded when the process goes on indefinitely, giving  .
.
Solution 3
Using Solution 1 as a template, note that the sum of the areas forms a geometric series:
This is the sum of a geometric series with first term  and common ratio
and common ratio  This is the easiest way to do this problem.
This is the easiest way to do this problem.
The sum of an infinite geometric series with  is shown by the formula.
is shown by the formula.  Insert the values to get
Insert the values to get  , giving an answer of
, giving an answer of  .
.
Art of Problem Solving
궁금한게 있으면 010-3549-5206으로..
궁금한게 있으면 010-3549-5206으로..

댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기