정리
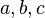 는 삼각형의 세 변의 길이라고 하고,
는 삼각형의 세 변의 길이라고 하고,  는 변
는 변 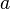 와 그 반대편의 꼭지점을 잇는 선분의 길이라고 하자.
와 그 반대편의 꼭지점을 잇는 선분의 길이라고 하자.  가 변
가 변 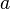 를 길이
를 길이  ,
, 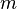 으로 나눈다고 하면, 다음 관계가 성립한다.
으로 나눈다고 하면, 다음 관계가 성립한다. 일 경우
일 경우  는 중선이 되고 이때 관계식은 중선정리가 된다.
는 중선이 되고 이때 관계식은 중선정리가 된다.증명
 는
는 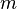 과
과  가 이루는 각이고,
가 이루는 각이고,  는
는  과
과  가 이루는 각이라 하자. 두 각을 합하면 180도 이므로 코사인의 성질 때문에
가 이루는 각이라 하자. 두 각을 합하면 180도 이므로 코사인의 성질 때문에  이다. 코사인 법칙에 의해 다음 식이 성립한다.
이다. 코사인 법칙에 의해 다음 식이 성립한다. 을 곱하고, 두 번째 식에
을 곱하고, 두 번째 식에 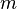 을 곱하여 더해서
을 곱하여 더해서 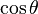 를 제거하면 다음을 얻는다.
를 제거하면 다음을 얻는다.Stewart's Theorem

Let a Cevian
Bottema (1979) extended the formula to simplices in higher dimensions, and Bottema (1980-1981) explicitly considered the tetrahedron.
Wolfram| MathWorld




댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기